This page summarizes my research activities including publications in academic journals and conference proceedings.
Papers
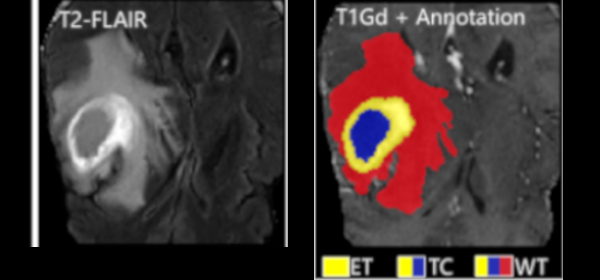
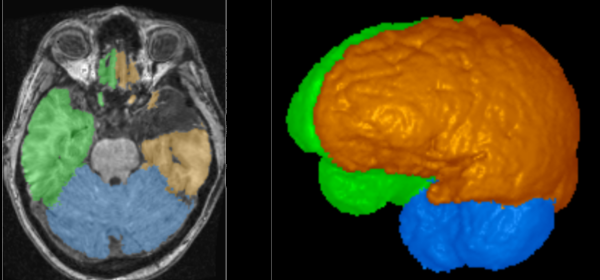
Federated Learning Enables Big Data for Rare Cancer Boundary Detection
Sarthak Pati, Samuel B. Martins, et al.
Nature Communications 13, 7346 (2022)
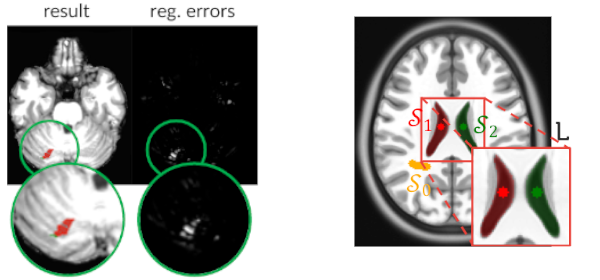
Published versionCombining Registration Errors and Supervoxel Classification for Unsupervised Brain Anomaly Detection
Samuel B. Martins, Alexandre X. Falcão, Alexandru C. Telea
Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies, Springer International Publishing, pp. 140–164, 2021.
Published versionBADRESC: Brain Anomaly Detection based on Registration Errors and Supervoxel Classification
Samuel B. Martins, Alexandre X. Falcão, Alexandru C. Telea
BIOSTECT BIOIMAGING, pp. 74-81, 2020.
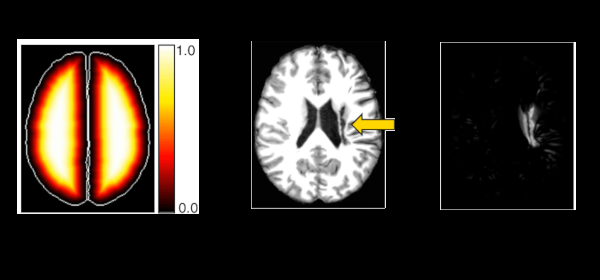
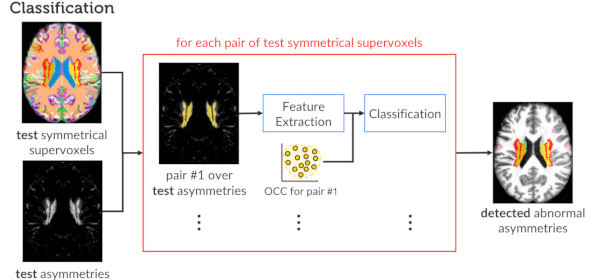
Published versionInvestigating the impact of supervoxel segmentation for unsupervised abnormal brain asymmetry detection
Samuel B. Martins, Alexandru C. Telea, Alexandre X. Falcão
Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, 85, pp. 101770, 2020.
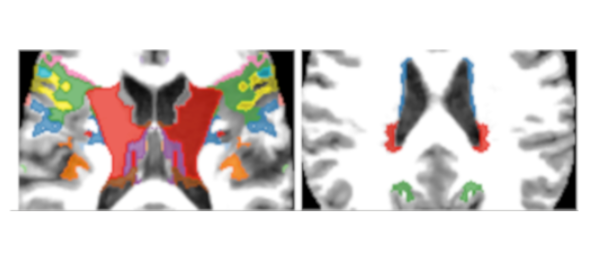
Published versionAn adaptive probabilistic atlas for anomalous brain segmentation in MR images
Samuel B. Martins, Jordão Bragantini, Alexandre X. Falcão, Clarissa L. Yasuda
Medical Physics, 46 (11), pp. 4940-4950, 2019.
Published versionMethods: In AdaPro, we first build one probabilistic atlas per object of interest from a training set with normal 3D images and the corresponding 3D object masks. Second, we incorporate a texture classifier based on convex optimization which dynamically indicates the regions of the target 3D image where the PAs (shape constraints) should be further adapted. This strategy is mathematically more elegant and avoids problems with post-processing. Third, we add a new object-based delineation algorithm based on combinatorial optimization and diffusion filtering. AdaPro can then be used to locate and delineate the objects in the coordinate space of the atlas or of the test image. We also compare AdaPro with three other state-of-the-art methods: an statistical shape model based on synergistic object search and delineation, and two methods based on multi-atlas label fusion (MALF).
Results: We evaluate the methods quantitatively on 3D MR-T1 brain images of 2T and 3T from epilepsy patients, before and after temporal lobe resections, and on the template and native coordinate spaces. The results show that AdaPro is considerably faster and consistently more accurate than the baselines with statistical significance in both coordinate spaces.
Conclusion: AdaPro can be used as a fast and effective step for brain tissue segmentation and it can also be easily extended to segment subcortical brain structures. By choice of its components, probabilistic atlas, texture classifier, and delineation algorithm, it can also be extended to other organs and imaging modalities.
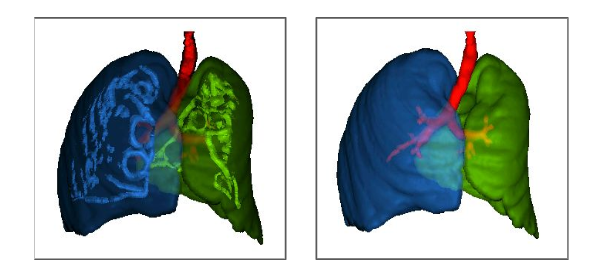
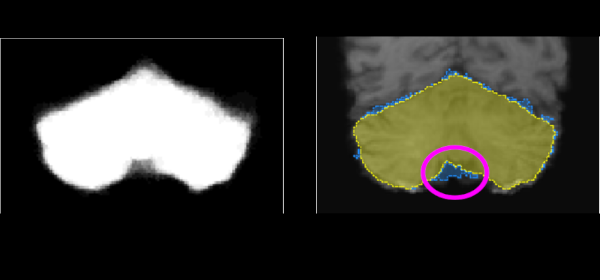
ALTIS: A fast and automatic lung and trachea CT-image segmentation method
Azael M. Sousa, Samuel B. Martins, Alexandre X. Falcão, Fabiano Reis, Ericson Bagatin, Klaus Irion
Medical Physics, 46 (11), pp. 4970-4982., 2019.
Published versionMethods: ALTIS consists of a sequence of image foresting transforms (IFTs) organized in three main steps: (a) lung-and-trachea extraction, (b) seed estimation inside background, trachea, left lung, and right lung, and (c) their delineation such that each object is defined by an optimum-path forest rooted at its internal seeds. We compare ALTIS with two methods based on shape models (SOSM-S and MALF), and one algorithm based on seeded region growing (PTK).
Results: The experiments involve the highest number of scans found in literature - 1255 scans, from multiple public data sets containing many anomalous cases, being only 50 normal scans used for training and 1205 scans used for testing the methods. Quantitative experiments are based on two metrics, DICE and ASSD. Furthermore, we also demonstrate the robustness of ALTIS in seed estimation. Considering the test set, the proposed method achieves an average DICE of 0.987 for both lungs and 0.898 for the trachea, whereas an average ASSD of 0.938 for the right lung, 0.856 for the left lung, and 1.316 for the trachea. These results indicate that ALTIS is statistically more accurate and considerably faster than the compared methods, being able to complete segmentation in a few seconds on modern PCs.
Conclusion: ALTIS is the most effective and efficient choice among the compared methods to segment left lung, right lung, and trachea in anomalous CT scans for subsequent detection, segmentation, and quantitative analysis of abnormal structures in the lung parenchyma and pleural space.
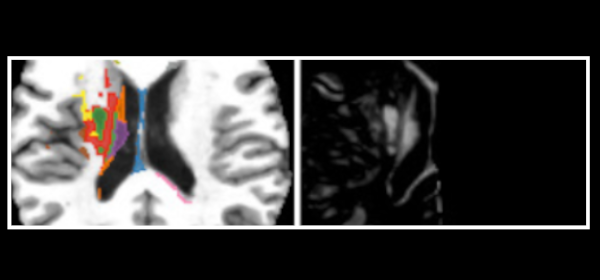
Extending Supervoxel-based Abnormal Brain Asymmetry Detection to the Native Image Space
Samuel B. Martins, Alexandru C. Telea, Alexandre X. Falcão
IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), IEEE, pp. 450-453, 2019.
Published versionA Supervoxel-Based Approach for Unsupervised Abnormal Asymmetry Detection in MR Images of the Brain
Samuel B. Martins, Guilherme Ruppert, Fabiano Reis, Clarissa L. Yasuda, Alexandre X. Falcão
International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), IEEE, pp. 882-885, 2019.
Published versionModeling normal brain asymmetry in MR images applied to anomaly detection without segmentation and data annotation
Samuel B. Martins, Barbara C. Benato, Bruna F. Silva, Clarissa L. Yasuda, Alexandre X. Falcão
SPIE Medical Imaging, vol. 10950, pp. 71-80, 2019.
Published versionGraph-Based Image Segmentation Using Dynamic Trees
Jordão Bragantini, Samuel B. Martins, Cesar Castelo-Fernandez, Alexandre X. Falcão
Iberoamerican Congress on Pattern Recognition (CIARP), Springer, pp. 470-478, 2018.
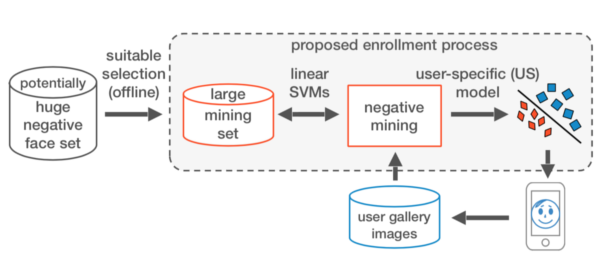
Published versionA Fast and Robust Negative Mining Approach for Enrollment in Face Recognition Systems
Samuel B. Martins, Giovani Chiachia, Alexandre X. Falcão
Conference on Graphics, Patterns and Images (SIBGRAPI), IEEE, pp. 201-208, 2017.
Published versionA multi-object statistical atlas adaptive for deformable registration errors in anomalous medical image segmentation
Samuel B. Martins, Thiago V. Spina, Clarissa L. Yasuda, Alexandre X. Falcão
SPIE Medical Imaging, pp. 101332G, 2017.
Published versionInteractive Medical Image Segmentation by Statistical Seed Models
Thiago V. Spina, Samuel B. Martins, Alexandre X. Falcão
Conference on Graphics, Patterns and Images (SIBGRAPI), IEEE, pp. 273-280, 2016.
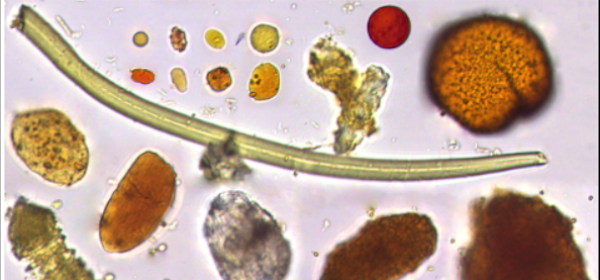
Published versionDiagnosis of Human Intestinal Parasites by Deep Learning
Alan Z. Peixinho, Samuel B. Martins, John E. Vargas, Alexandre X. Falcão, Jeancarlo F. Gomes, Celso T. N. Suzuki
Eccomas Thematic Conference on Computational Vision and Medical Image Processing (VipIMAGE), 2015.
Published versionMedical image segmentation using object shape models: A critical review on recent trends, and alternative directions
A. X. Falcão, T. V. Spina, S. B. Martins, R. Phellan
Eccomas Thematic Conference on Computational Vision and Medical Image Processing (VipIMAGE), 2015.
Published versionReviews
I have been acting as an expert reviewer at the following academic outlets: